Early Treatment
It is never too late to begin orthodontic treatment, but when it comes to your youngster’s teeth, did you know that earlier may be better? The American Association of Orthodontists® recommends that children receive their first orthodontic screening by age 7, and we encourage you to bring your child to our office by this age to evaluate their need for orthodontic treatment.
When Earlier Treatment is Better
Treatment for common orthodontic problems typically begins around age 9-14, when all of the baby teeth are gone and many of the permanent ones are in place. But there are some conditions that are much easier to treat if they’re caught at an early age, when a child’s natural growth processes are going full speed ahead.
One is severe crossbite, a condition where the upper teeth close inside the lower teeth. To treat this problem, a device called a palatal expander can be used, which gradually and painlessly widens the upper jaw; it’s especially effective when the jaw itself hasn’t fully developed. If we wait too long, a more complicated treatment — or even oral surgery — might be required to correct the problem.
Another condition that may benefit from early treatment is severe crowding. This occurs when the jaws are too small to accommodate all of the permanent teeth. Either palatal expansion or tooth extraction may be recommended at this point, to help the adult teeth erupt (emerge from below the gums) properly. Even if braces are required later, the treatment time will likely be shorter and less complicated.
Early intervention may also be helpful in resolving several other problems. Protruding teeth, especially in front, can be prone to chipping and fractures; they may also lead to problems with a child’s self-image. A severe underbite, caused by the lower jaw growing much larger than the upper jaw, can result in serious bite problems. Orthodontic appliances, including braces and headgear, can be successfully used to correct these problems at this stage, when the child’s development is in full swing, thereby increasing the chances that surgery can be avoided.
Correcting Bad Habits
At one time or another, anyone may pick up a bad habit. But there are some situations where a youngster’s parafunctional (detrimental to health) habits can actually influence the development and function of his or her teeth, jaws and mouth. Some examples of these are persistent thumb sucking, tongue thrusting and mouth breathing.
The sucking reflex is natural in early childhood; it usually disappears between ages 2 and 4. But if it persists much later, the pressure of the digit on the front teeth and the upper jaw can actually cause the teeth to move apart and the jaws to change shape. This can lead to the orthodontic problem called “open bite,” and may impair speech. An open bite can also be caused by the force of the tongue pushing forward against the teeth (tongue thrusting).
Mouth breathing — an abnormal breathing pattern in which the mouth always remains open, passing air directly to the lungs — is related to alterations in the muscular function of the tongue and face. It may cause the upper and lower jaw to grow abnormally, which can lead to serious orthodontic problems. Although mouth breathing may start from a physical difficulty, it can become a habitual action that’s hard to break.
Various orthodontic treatments are available to help correct these parafunctional habits — and the sooner they’re taken care of, the less damage they may cause. But these potential problems aren’t always easy to recognize. That’s one more reason why you should bring your child in for an early orthodontic screening.
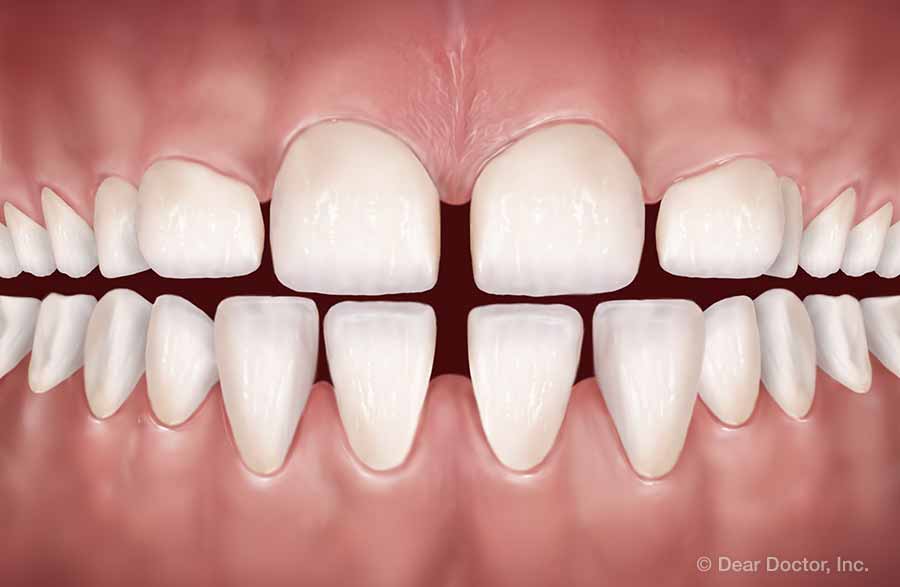 Crossbite
Crossbite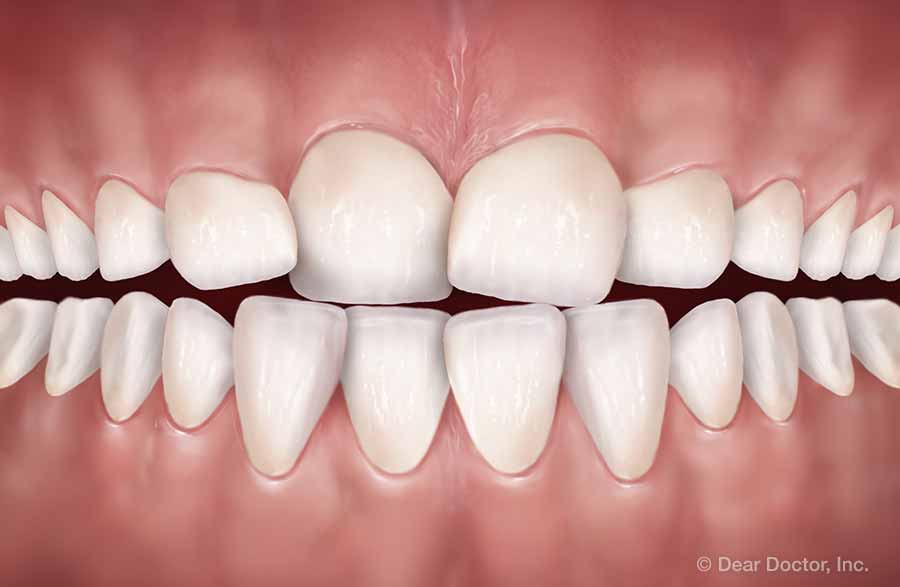 Crowding
Crowding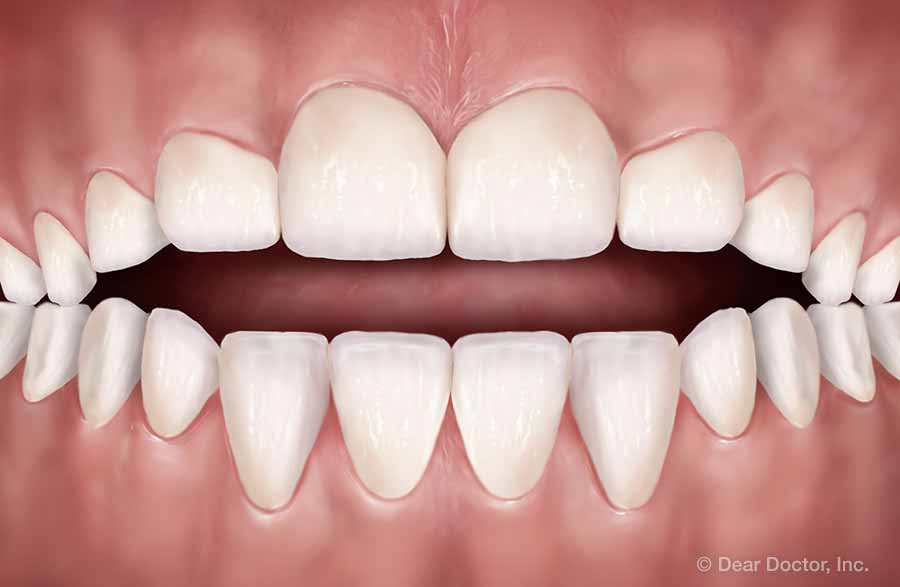 Open Bite
Open Bite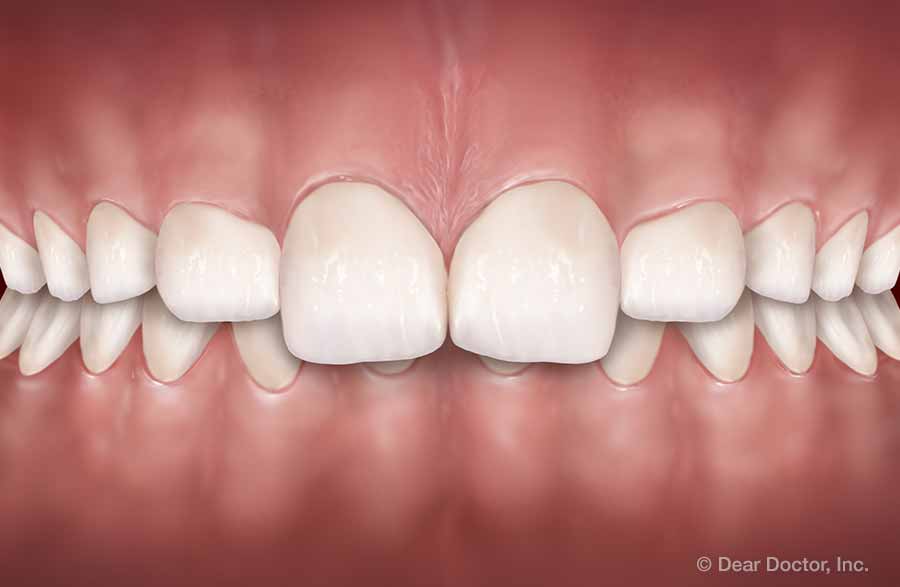 Overbite (Deep Bite)
Overbite (Deep Bite)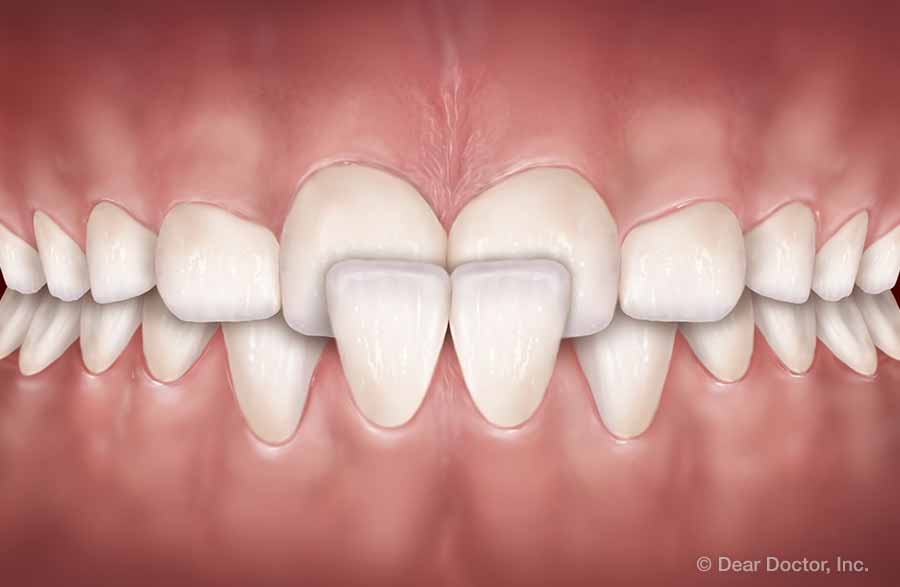 Crossbite (Front Teeth)
Crossbite (Front Teeth)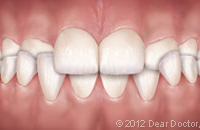 Crossbite (Back Teeth)
Crossbite (Back Teeth)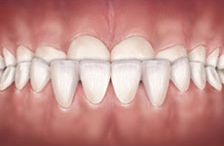 Underbite
Underbite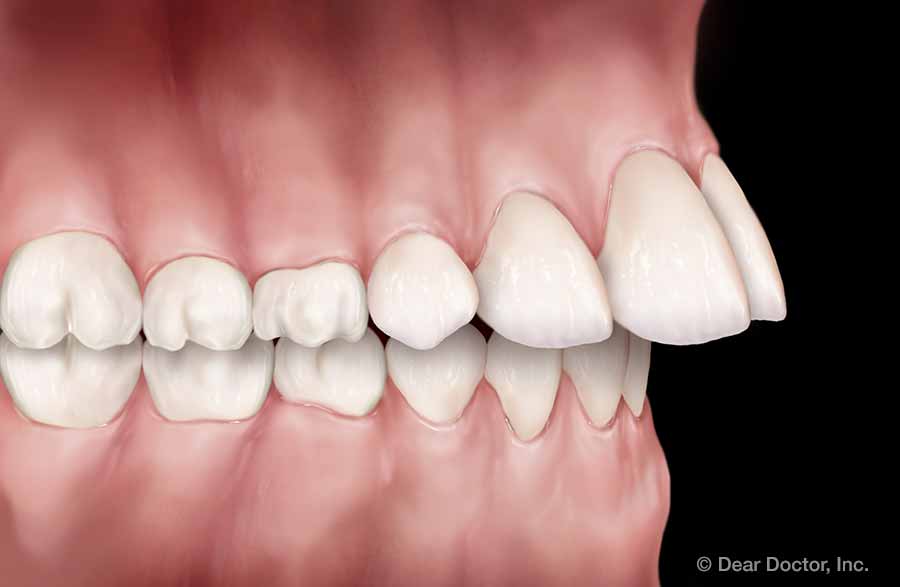 Overjet (Protrusion)
Overjet (Protrusion)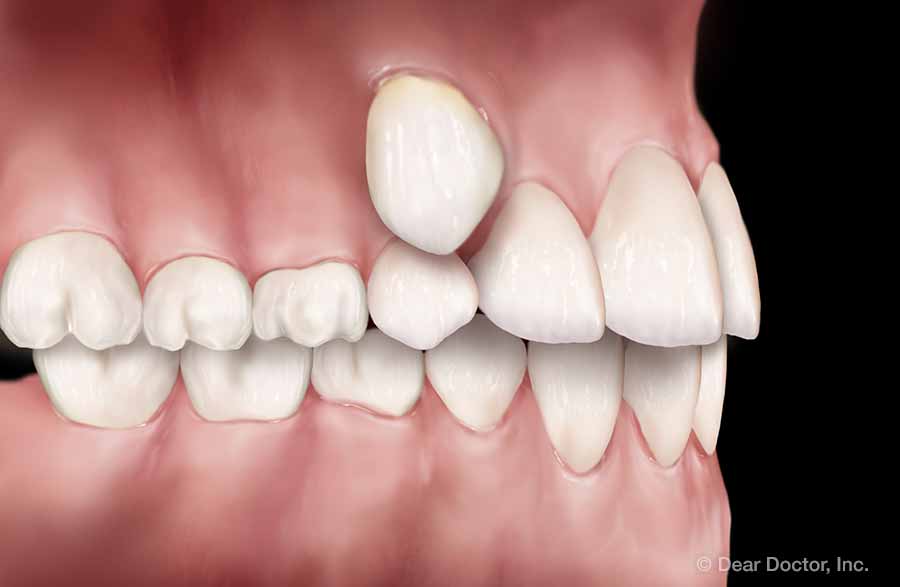 Abnormal Eruption
Abnormal Eruption








